Hydrogen can connect the entire energy system – from renewable electricity generation to storage, industry and transport. By converting electricity into hydrogen, energy can be stored for a long time and used when and where it is needed. In this way, hydrogen becomes a link between the electricity grid, industry and the transport sector, and a key to creating a sustainable and fossil-free energy system.
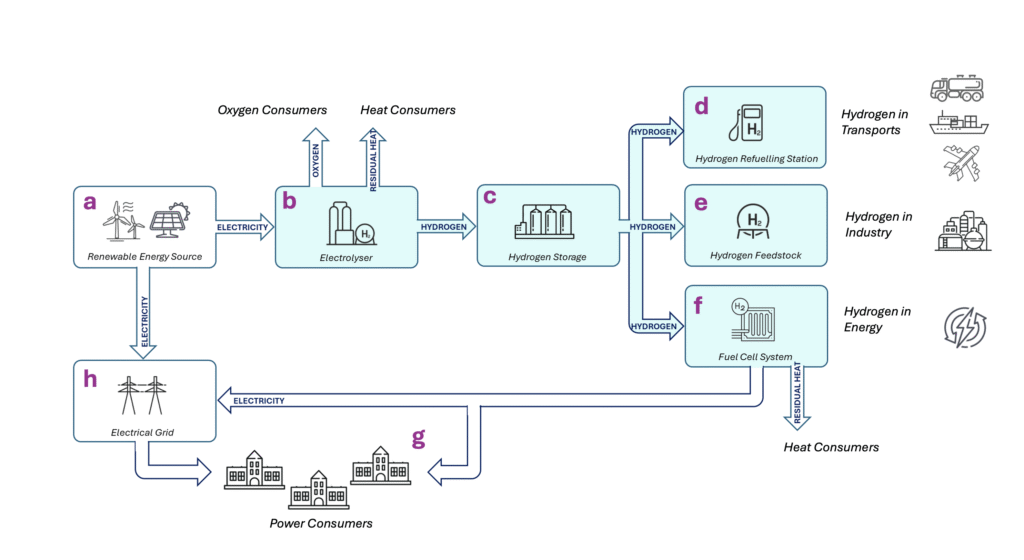
a. Renewable Energy Source
Hydrogen starts its journey with renewable energy from wind, solar or hydropower, for example. The electricity produced here can either be fed into the grid or used directly to produce hydrogen through electrolysis. When the electricity is used to produce hydrogen, the result is called renewable or green hydrogen, as no fossil fuels are used in the process.
b. Electrolyzer
In the next step, electricity is used to split water (H₂O ) into its components: hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂). The process takes place in an electrolyzer, which works much like the reverse of a fuel cell. In addition to hydrogen and oxygen, waste heat is also generated and can be used in district heating systems or other local heating plants.
c. Hydrogen Storage
The hydrogen produced can be stored in different forms – as compressed gas, liquid hydrogen or in underground caverns. Storing hydrogen helps balance energy supply and demand, as the energy can be stored for weeks or months and used when electricity production from solar and wind is low.
d. Refueling stations for vehicles – Hydrogen Refueling Station
From the storage, the hydrogen can be used as vehicle fuel. At refueling stations, hydrogen is compressed to high pressures and filled into fuel cell vehicles – such as cars, buses, trucks, ships and, in the future, aircraft. When these vehicles are running, they only emit water vapor, making the transport sector completely free of local emissions.
e. Raw material for industry – Hydrogen Feedstock
Hydrogen is also used as a raw material in industry, particularly in the steel, chemical and refinery sectors. By replacing fossil fuels or coal with hydrogen, industry can significantly reduce its carbon emissions. One example is fossil-free steel, where hydrogen is used to reduce iron ore instead of coal.
f. Fuel Cell System – Fuel Cell System
In the fuel cell, the process is reversed compared to electrolysis. It combines hydrogen and oxygen in an electrochemical reaction that produces electricity, heat and water, with no combustion and no CO2 emissions. Fuel cells are used both in vehicles and in stationary systems for local electricity and heat production.
g. Power Consumers
Electricity produced in fuel cells or directly from renewable sources is used by households, industries and public services. Hydrogen allows renewable energy to be distributed and used efficiently over time, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and increasing the flexibility of the energy system.
h. Elnätet – Electrical Grid
The renewable energy system is linked by the electricity grid, which supplies electricity to society and can also power the electrolysers when there is a surplus of renewable electricity. In this way, hydrogen acts as a link between the electricity system, industry and the transport sector – a key component of a sustainable, circular and robust energy system.